When Esquire announced that electronic transcripts would replace sealed paper originals in California, it framed the move as sustainability. Regulators later confirmed it was illegal. A CRB investigation found the policy violated long-standing California law and was reversed only after a formal complaint. The episode exposes how easily corporate workflow changes can endanger reporters’ licenses—and why knowing the code matters before real damage is done.
Tag Archives: TranscriptIntegrity
Courts Do Not Have an AI Problem. They Have a Record-Keeping and Accountability Problem.
Courts do not face an artificial intelligence crisis so much as a crisis of accountability. AI-related errors expose gaps in supervision, verification, and professional responsibility, not rogue technology. Judicial legitimacy is not threatened by tools, but by inconsistent governance. The question before the courts is not whether AI will be used, but whether responsibility will remain clearly human.
You Can’t Stipulate Your Way Around the Law – The Dangerous Fiction of the “No-Reporter Stipulation”
A court transcript is not a convenience. It is evidence. When attorneys stipulate to proceed without a court reporter, they are not authorizing an “alternative record.” They are agreeing that no lawful evidentiary record will be created. What follows—a stipulated statement of proceedings—is not a transcript, but a negotiated reconstruction. And evidence cannot be manufactured after the fact.
When Machines Become Witnesses – Why the Federal Judiciary’s AI Evidence Proposal Quietly Reinforces the Role of Court Reporters
The federal judiciary’s proposed rule on AI-generated evidence quietly draws a critical line: machine output is not inherently trustworthy and must be tested like expert testimony. That distinction reinforces the structural role of court reporters. A certified transcript is a human-governed legal record, not algorithmic evidence. Once the human layer disappears, the court record itself becomes something the law now admits is dangerous.
Remote Reporting Didn’t Devalue the Profession. It Forced It to Clarify Its Value.
Remote proceedings did not cheapen court reporting. They stripped away logistics and forced the profession to confront what it actually sells: custody of the legal record. As rate debates intensify, the future of stenography may depend less on where reporters sit and more on whether the profession anchors its value in accountability, professional responsibility, and the integrity of the record itself.
The Readback Problem in Voice Writing—and How to Solve It
Readback is where the record proves its reliability. For voice writers, that moment too often collapses into rewind and guesswork when ASR fails. The solution is not better training, but better software: a persistent phonetic fallback, confidence-aware output, and word-level audio that function like steno notes. Voice does not need perfection—it needs an inspectable substrate.
If You Want Lower Transcript Costs, Help Create More Court Reporters
Transcript prices are not rising because court reporters are greedy; they are rising because there are fewer of them. Like any market, court reporting follows basic economic rules: when supply shrinks and demand grows, prices increase. If attorneys want lower transcript costs, the solution is not cheaper capture methods—it is helping rebuild, retain, and respect the human court reporting workforce.
Who Trained the Machine?
AutoScript AI is marketed as a “legal-grade” AI transcription solution trained on “millions of hours of verified proceedings,” yet the company provides no public definition of what verification means in a legal context or where that data originated. Founded and led by technology executive Rene Arvin, the platform reflects a broader trend of general ASR tools being rebranded for legal use without the transparency traditionally required in court reporting.
The Bubble Beneath the Record – A Financial Crisis in Court Reporting Is Coming
A financial bubble is forming beneath the court reporting industry. Private equity markups have pushed attorneys toward cheaper “alternative” record methods, but those substitutes fail evidentiary standards and are beginning to collapse under legal scrutiny. As reporters reject unsustainable rates and attorneys realize uncertified transcripts don’t hold up in court, the industry is nearing a correction. The record cannot be commodified—and the bubble will burst.
Why Transcript Correction Disputes Are Rising — And Where the Problem Originated
Certified court reporters are seeing a rise in large-scale transcript correction requests, but the issue is not declining reporter skill. It stems from the increased use of digital audio and ASR-generated transcripts being treated as equivalent to stenographic reporting. Once attorneys began comparing transcripts with software tools, the inconsistencies became clear. Accuracy starts at the point of capture, and the method matters.
The Court Reporting Industry Faces Structural Stress
The court reporting sector is showing signs of structural stress after years of private-equity consolidation and rising interest rates. Higher transcript costs and declining reporter compensation have prompted some firms to explore lower-cost recording methods, though many of these alternatives face evidentiary and certification limits. As labor supply tightens and compliance standards remain unchanged, the market appears to be shifting back toward models emphasizing reliability and credentialed recordkeeping.
When a Video Is Played in Court – How to Handle, Certify, and Communicate It Professionally
When an attorney asks you to “take down” a video played in court, your authority comes from Rule 2.1040(d)—not the attorney. Always obtain a court order, mark the playback as a “transcription of an electronic recording,” and certify it separately. This protects your license, the record’s integrity, and your professional credibility while keeping the attorneys—and the judge—happy.
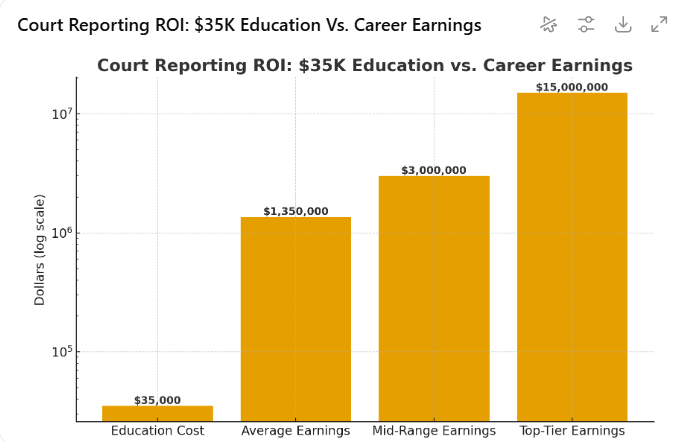
Court Reporting is the $35,000 Investment That Can Yield Millions
Court reporting may be the smartest career investment few people talk about. For about $35,000 in education, reporters can earn anywhere from $45,000 a year on average to $500,000+ at the top of the field. That’s a lifetime income range of $1.35 million to $15 million. Even at the low end, the ROI far outpaces most college degrees.